
Petersburg, which was consequently sent to someone in France. This may have been the one Kratzenstein sent to the Academy in St. Apparently, he had seen an instrument built by Kratzenstein 30 years earlier at a friend’s house, around 1770, which led to his own application of the operating principle. In 1810, Gabriel Joseph Grenié of Paris applied for a patent for his “orgue expressif” and was thus the first to introduce the reed organ in his country. This type of dynamic was exactly what performers and composers were looking for, and the music of Beethoven and Berlioz testify to the new kind of massive dynamic range approaches that were becoming very popular. The tremendous dynamic range of the reeds with windpressure, from very soft and nearly inaudible (a feature not possible with classic pipe organ reeds) to quite loud, mimicked the dynamic range of the then still new pianoforte as an organ. Petersburg, like Johann Gabrahn, started to make "claviorganums." The news of this new type of instrument quickly spread to Germany, where, possibly among others, Strohmann and Abbe Vogler further developed these types of instruments. As far as is known, it was not applied to any classic pipe or church organ. This was the first time that free floating reeds were employed as a new kind of organ stop. Kirschnick then decided independently to use these kinds of reeds in his instruments, such as the pianoforte/organ combinations (called claviorganum), and possibly in an instrument called the "orchestrion," an automatic player or barrel type organ, around 1781. He may have worked together with organ builder Franz Kirschnick and his assistant, Georg Christoffer Rackwitz. Kratzenstein, thus, sent a small two-octave reed instrument to the Academy of Science in St. The free floating reed was developed in 1778, by Christian-Gottlieb Kratzenstein (1723-1795) as part of a plan to construct a human speech machine that could mimic the vowels of human speech for scientific research. Original invention by Kratzenstein for scientific research Reed organs, or American organs, as they are called in the United States, became very popular, and many factories sprung up in the second half of the nineteenth century when these instruments were mass-produced.
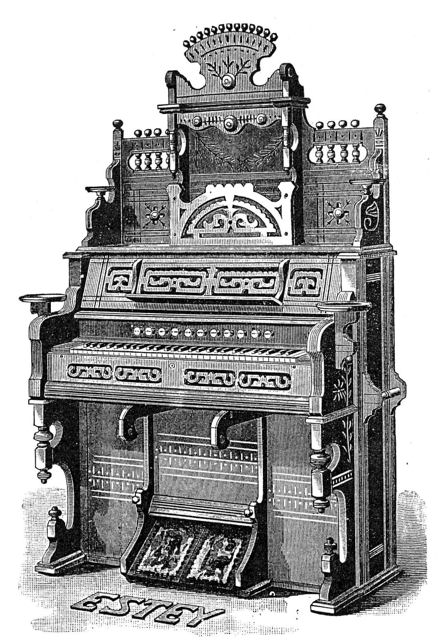
They were also popular in homes and businesses since these were instruments that reminded people of church organs or keyboard instruments in popular singing groups. Since they were less expensive to build, lighter than pianos, and didn’t need tuning, many found their way well outside Europe and North America. Suction type organs were mainly built in the United States, but European makers later followed as well.

Most pressure wind type reed organs were built in Europe, although the American builder Aeolian made many Vocalion models with two manuals and an independent pedal with its own keyboard.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
